Faculty

Aditya Murthy
ProfessorOffice : Ground floor of PRL at Central Animal Facility
Phone : +91 80 2293 3290
E-Mail : adi[at]iisc.ac.in
web : www.cns.iisc.ac.in/aditya/
Research Areas
Movement Control
Research Details
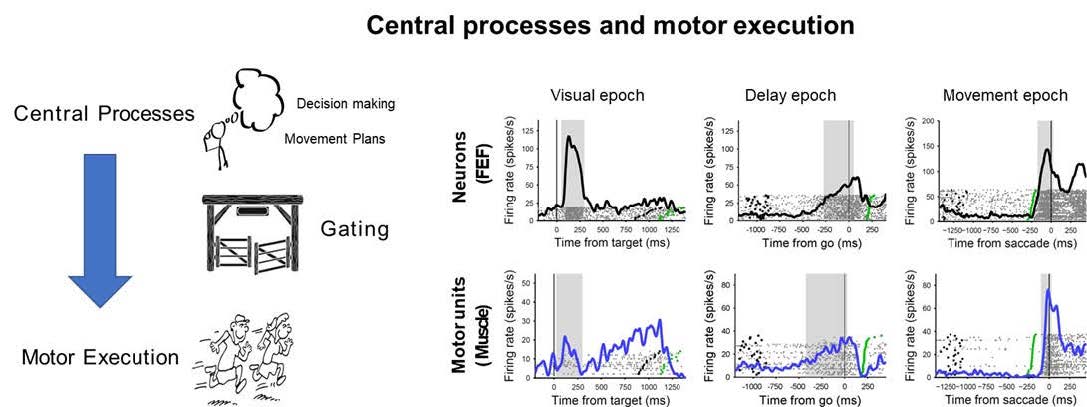
All goal directed behaviour whether it involves playing an instrument or singing a song involves the precise coordination and control of many muscles together. For this to occur, the brain must decide, plan, execute and get feedback on the movement. The lab seeks to understand the computations that enable goal directed behaviour with an emphasis to understand the basis of flexibility and control that is the hallmark of intelligent action. Our research interests span the fields of visual perception, decision-making, and the generation of motor behavior and involve the application of cognitive/psychophysical, neuropsychological, and electrophysiological techniques.
Currently, the lab uses a combination of high-density surface EMG recordings during voluntary movements to probe and test the relationship between the patterns of motor unit recruitment and movement initiation and control using behavioral and neurostimulation approaches in normal human subjects and those with motor disorders such as Parkinson’s Disease. Besides giving insight into how information processed in motor areas is read out by muscles during voluntary movements, we wish to delineate the neural basis of flexible sensorimotor gating. We hope that such a line of research could be used to develop novel treatments for motor disorders and develop assistive non-invasive brain-machine interfaces.